We frequently receive requests to sort HubDB rows based on our clients' specific needs and the data they want to display. Mastering the art of sorting and filtering rows in HubDB can greatly improve the user experience and make data more easily accessible.
In this article, we are going to examine several common methods to display HubDB table data using HubL functions built in sorting features.
To get started, we'll need to create a HubDB table.
Imagine you want to showcase job listings on a careers page - you can easily set up a table like the one below. Let's take a look at the table data we'll be working with.
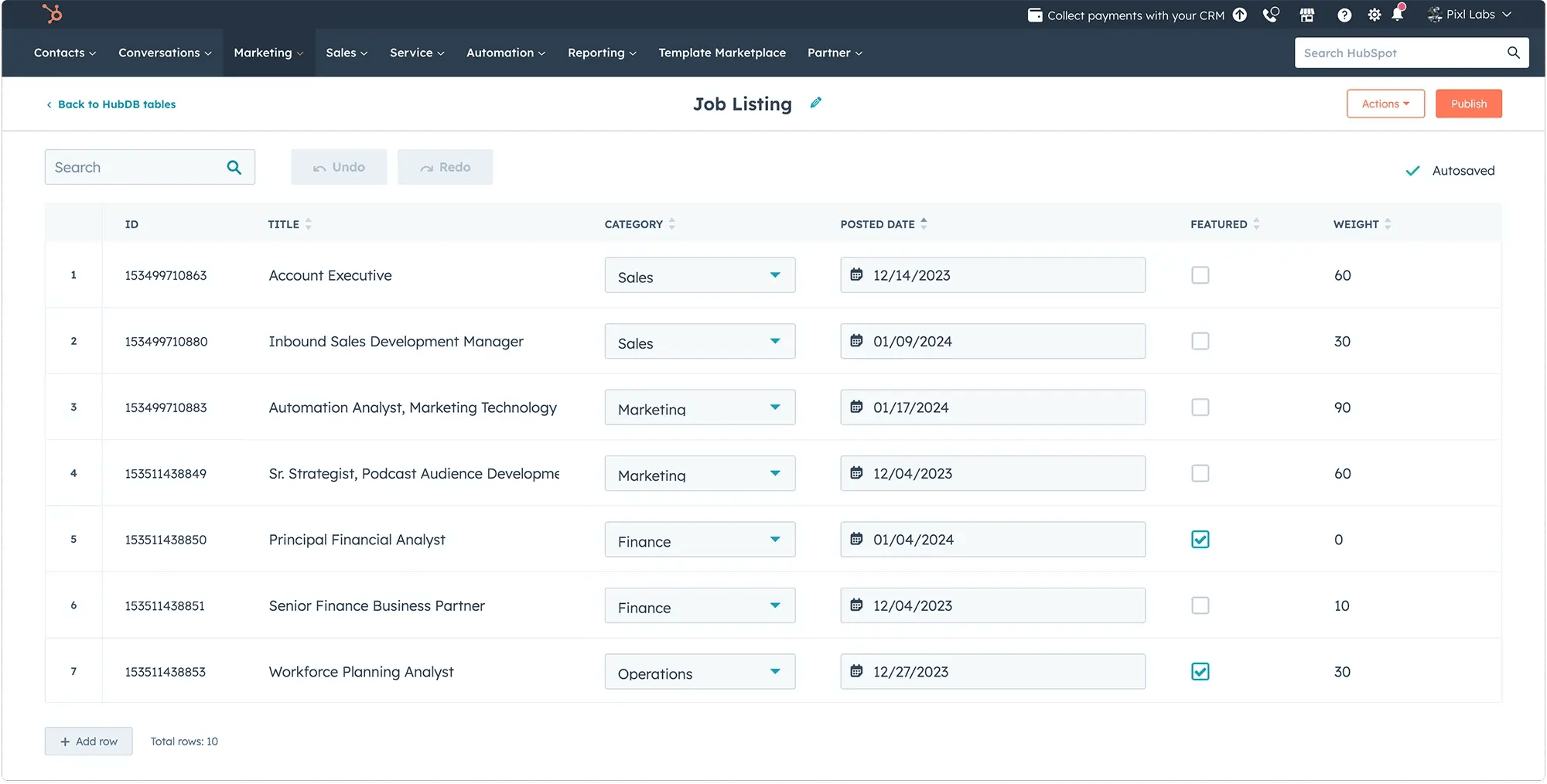
We have a HubDB of job listings with the following fields:
- Title (text field)
- Posted Date (date field)
- Featured (boolean field)
- Weight (number field)
While there are numerous field types to choose from in HubDB, the ones mentioned above are the most frequently utilized for sorting rows.
When you create a new HubDB table, the ID and name columns are included by default.
Using hubdb_table_rows
There are two methods for calling HubDB row data:
Although the sorting methods are similar, we will cover how to utilize the API in a future article. For now, we will focus on using HubL functions within a module to display our data anywhere on our site.
The HubL function we will use is hubdb_table_rows(). This function accepts the following two parameters:
- table name or id - (required)
- query - (optional);
In its most basic form, using this function would look like this:
This default order is identical to how the rows are displayed in the HubDB table.
A recent update to HubDB added the ability to drag the rows into any sort that you want. This DOES affect the default sort when using hubdb_table_rows()
Sort by Ascending vs. Descending
Rows can be sorted either ascending or descending, based on the parameters passed through the query string. The two main types of content used for sorting and their related fields in our example are:
- Alphabetical (String) - Text, Boolean
- Numeric (Integer) - Date, Number
The default for these is always ascending (i.e. [0-9][A-Z]).
To reverse this you just need to add a - sign before the column name in the query string. For example: “orderBy=-title”.
Ordering by a Text Field
Text fields are the most common sorting method for a majority of use cases. To do this, we are using our job title.
Ordering by Boolean
If we want to feature a couple specific jobs over the rest, then we can use a boolean. Our field is the aptly named featured.
Since booleans are sorted alphabetically, the ascending order will put the false value first. Since we want our featured jobs to show before the others, we need to reverse the query.
Ordering by a Date Field
Since we are displaying job listings, a date field is a very common sorting method for our use case because we can use it to display the older job postings first to try and get them filled.
Date and datetime fields utilize Unix Timestamp under the hood, so though it may seem daunting, they sort just like any other integer.
Ordering by Weight (custom)
If you need to sort your rows by specific groups that none of the other methods cover then you can create a new number field and customize which rows go in which group.
Ordering by Multiple Queries
Let’s say you want to order by the featured and by the most recent based on the "posted date" field. We can accomplish this by chaining together two or more queries to nest multiple sorting methods.
Now the featured and unfeatured listings are separated and they are all still sorted by oldest posting date first.
We hope that this article has provided valuable insights and guidance on effectively showcasing your HubDB content. While you're here, don't forget to explore some of the other HubSpot development articles below!
Receive resources directly to your inbox
Sign up to get weekly insights & inspiration in your inbox.